Implementing Infinite scroll in React apps
Step-by-step guide on integrating the 'react-infinite-scroll-component' in your React application.
Infinite scroll is a technique that loads content continuously as the user scrolls down the page, eliminating the need for pagination. This approach can enhance user engagement and time spent on the site, making it a popular choice for social media platforms and content-heavy applications. This blog aims to guide React developers through the implementation of infinite scroll in their applications using the react-infinite-scroll-component library.
Understanding the basics
Infinite scroll works by triggering an event as the user approaches the bottom of the content. This event initiates a request to fetch more content, which is then appended to the existing content. Unlike pagination, which divides content into discrete pages, infinite scroll offers a fluid, uninterrupted browsing experience.
Setting up the project
Start by creating a new React project using Vite:
npm create vite@latest
After setting up the project, install the react-infinite-scroll-component library:
npm i react-infinite-scroll-component
Install the axios library to make API requests:
npm install axios
Implementing infinite scroll
We will be using the Rick and Morty API to demonstrate infinite scroll. We will be fetching characters from the API on an infinite scroll event and displaying them in a list of cards.
I'll be using Material UI for styling the cards. You can install it by visiting the Material UI installation guide.
Let's start by creating a basic CharacterCard component:
import Card from "@mui/material/Card";
import CardHeader from "@mui/material/CardHeader";
import Avatar from "@mui/material/Avatar";
export default function CharacterCard({ character }) {
return (
<Card
sx={{
maxWidth: 345,
background: "black",
color: "white",
margin: "10px",
borderRadius: "10px",
}}
>
<CardHeader
avatar={<Avatar src={character?.image} aria-label="recipe"></Avatar>}
title={character?.name}
subheader={`Status: ${character?.status}`}
/>
</Card>
);
}
Next, in your App.js file, implement the infinite scroll functionality:
- We will be defining a few states for our
characters,pages, thetotalPageCountand abooleanstate to determine if we need to fetch more characters.
const [characters, setCharacters] = useState([]);
const [page, setPage] = useState(1);
const [hasMore, setHasMore] = useState(true);
const [totalPages, setTotalPages] = useState(1);
Here, characters will store the fetched characters, page will keep track of the current page number, hasMore will determine if there are more characters to fetch, and totalPages will store the total number of pages.
We will initialize totalPages by 1 initially and then after each subsequent call, we will update the state with the value from the API response.
- Next, we will define a function
fetchDatato fetch characters from the API:
const fetchData = async () => {
if (page == totalPages + 1) {
setHasMore(false);
return;
}
// <----------------------------------------------->
// waiting for 1 second before fetching data to show loading spinner, you can skip this
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
// <----------------------------------------------->
const res = await axios.get(
`https://rickandmortyapi.com/api/character?page=${page}`
);
setCharacters((prevPosts) => [...prevPosts, ...res.data.results]);
setTotalPages(res.data.info.pages);
setPage((prevPage) => prevPage + 1);
};
Here, we are fetching characters from the API and appending them to the characters state. We are also updating the totalPages and page states accordingly.
I am adding a delay of 1 second before fetching data to show the loading state properly and better understand the infinite scroll functionality. You can skip this if you want.
We will stop fetching data when the page reaches the totalPages + 1. At this point, we will set hasMore to false.
- Finally, we will implement the
InfiniteScrollcomponent:
<InfiniteScroll
dataLength={characters.length}
next={fetchData}
hasMore={hasMore}
loader={<h4>Loading...</h4>}
endMessage={
<p>
<b>Yay! You have seen it all</b>
</p>
}
>
{/* Map over characters array and return JSX */}
{characters.map((character, index) => (
<CharacterCard key={index} character={character} />
))}
</InfiniteScroll>
The InfiniteScroll component takes the following props:
dataLength: we set the length of data to determine when to trigger thenextfunction.next: the function to call when the user scrolls to the bottom of the page.hasMore: a boolean value to determine if there is more data to fetch.loader: a loading spinner to display while fetching data.endMessage: a message to display when all data has been fetched.
We can also add some extra props to the InfiniteScroll component to customize the behavior according to our requirements. You can read more about the react-infinite-scroll-component library here.
- Next, we will call the
fetchDatafunction when the component mounts:
useEffect(() => {
fetchData();
}, []);
This will fetch the initial set of characters when the component mounts.
App.jsshould look something like this:
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
import "./App.css";
import InfiniteScroll from "react-infinite-scroll-component";
import CharacterCard from "./components/Card";
function App() {
const [characters, setCharacters] = useState([]);
const [page, setPage] = useState(1);
const [hasMore, setHasMore] = useState(true);
const [totalPages, setTotalPages] = useState(1);
const fetchData = async () => {
if (page == totalPages + 1) {
setHasMore(false);
return;
}
// <----------------------------------------------->
// waiting for 1 second before fetching data to show loading spinner, you can skip this
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
// <----------------------------------------------->
const res = await axios.get(
`https://rickandmortyapi.com/api/character?page=${page}`
);
setCharacters((prevPosts) => [...prevPosts, ...res.data.results]);
setTotalPages(res.data.info.pages);
setPage((prevPage) => prevPage + 1);
};
useEffect(() => {
fetchData();
}, []);
return (
<div
style={{
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "center",
flexDirection: "column",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<h1>Rick and Morty characters!</h1>
<InfiniteScroll
dataLength={characters.length}
next={fetchData}
hasMore={hasMore}
loader={<h4>Loading...</h4>}
endMessage={
<p>
<b>Yay! You have seen it all</b>
</p>
}
>
{/* Map over characters array and return JSX */}
{characters.map((character, index) => (
<CharacterCard key={index} character={character} />
))}
</InfiniteScroll>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
We are now ready to test the infinite scroll functionality in our React application. Run the project using npm run dev and scroll down to see the infinite scroll in action. You should see something like this:
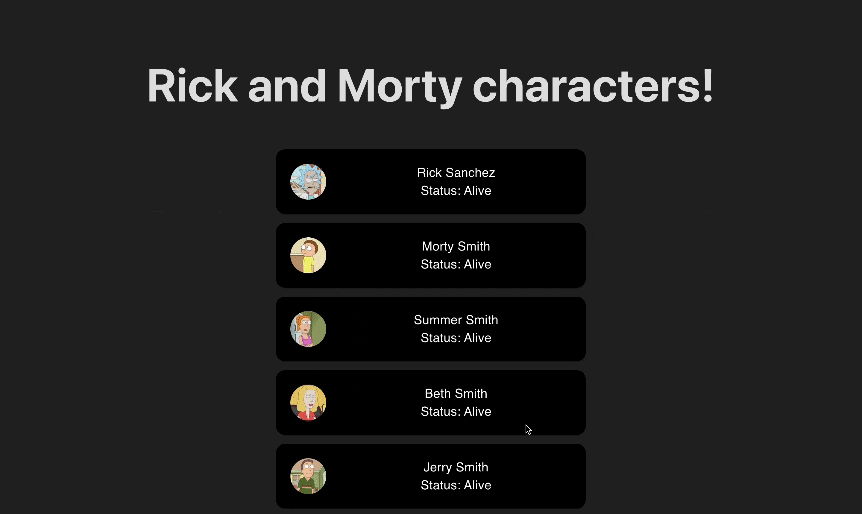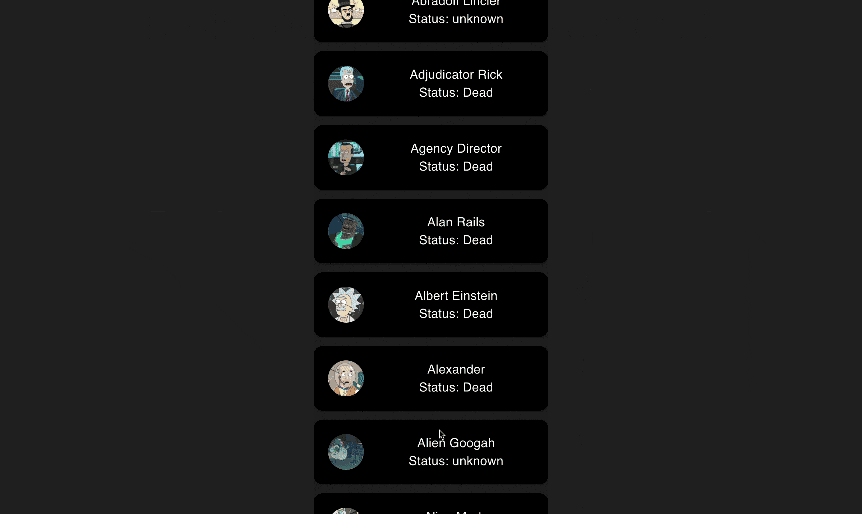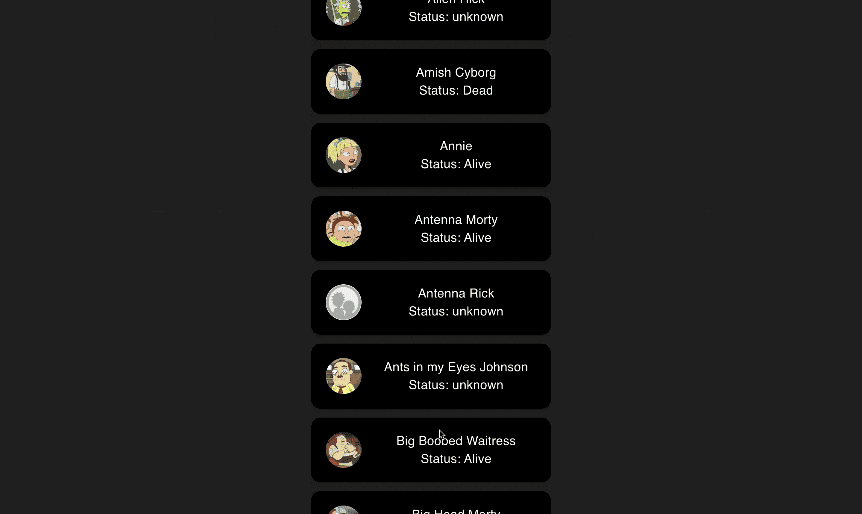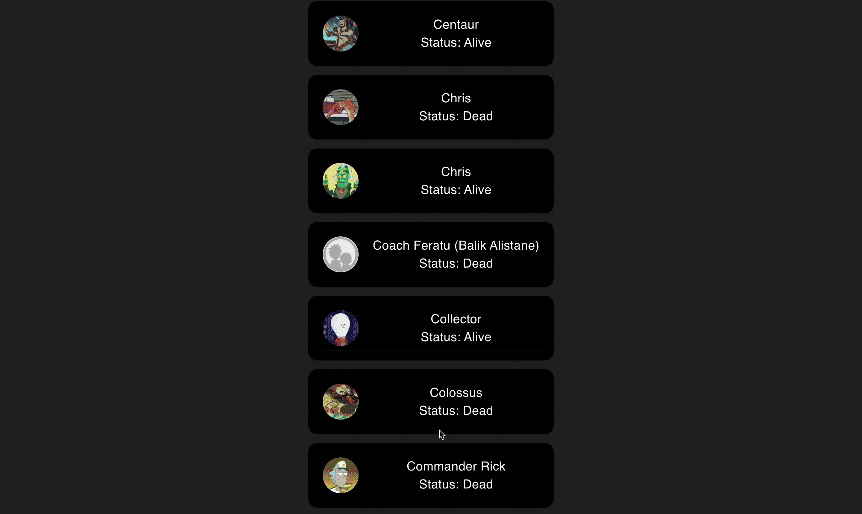
Conclusion
Infinite scroll is a powerful technique that can enhance user experience by providing a seamless browsing experience. By implementing infinite scroll in your React applications, you can create engaging and dynamic user interfaces that keep users coming back for more. The react-infinite-scroll-component library simplifies the process of implementing infinite scroll, making it easy for developers to add this feature to their applications. I hope this guide helps you get started with infinite scroll in your React projects. Happy coding!

